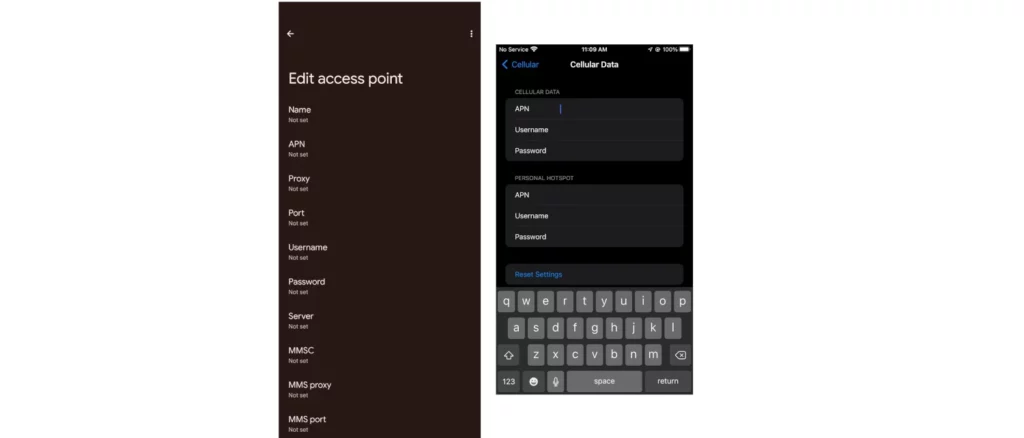
Access Point Name (APN) is a setting on every mobile device that connects to mobile network or the internet. These settings are necessary for identification of the right network and services provided by the network. APN is specifically the name of the gateway that it connects to.
For this reason, there are very many fields that need to be set. Some mobile network operators only require one field to be set, that is normally the APN field. The rest are automatically set up. proxy for example is the address of the server that data traffic is routed to. Username and password authenticate the connection to this server.
Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS) settings are also normally set up here. The fields for MMS are the MMSC, MMS Proxy, MMS Port and the APN Type is normally indicated as mms.
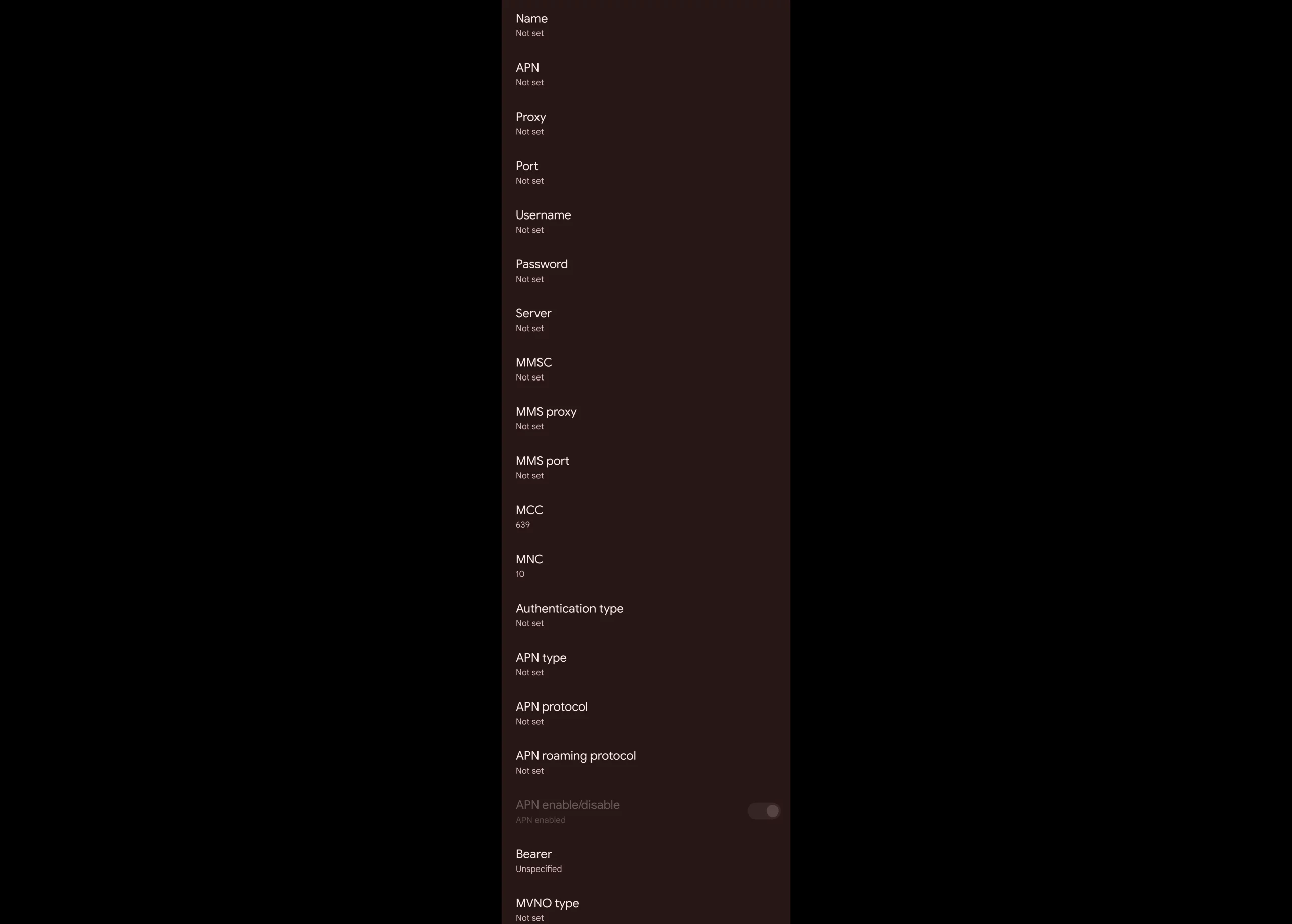
Access Point Name (APN) Fields
Access Point Name (APN) fields and their meanings together with popular values for different countries and mobile network operators.
Name
This option is a string of characters, normally your mobile network operator’s name, that you can easily use to tell APNs apart. You can set any name for this section as it is just an identifier for you that is human readable.
APN
Access Point Name (APN) is the name of the gateway at your mobile network operator that allows your mobile device to connect to the network and the internet. It also allows the identification of services on the network. This is normally the base and compulsory setting on the APN for it to work.
If you are in the United States, the common setting of APN is NXTGENPHONE, fast.t-mobile.com, vzwinternet, wholesale, reseller or pwg.
Proxy
Proxy is an intermediate server that sits between client device and server that receives and forwards requests. This speeds up web browsing, improves privacy and optimizes network usage.
Some mobile network operators leave this empty. Check with your operator for details if any.
Port
Port under APN settings is sometimes necessary for accessing certain services, bypassing restrictions or enhancing restrictions. It is important to note that not all mobile network operators require or have to use it.
The common APN port is 8080 or 80. A good number of mobile operators leave this blank.
Username
Username and password fields are normally used for authentication when proxy servers are used. It is also for authenticating other services on the network like a virtual private network (VPN).
Many mobile network operators do not use this and are normally left blank.
Passord
The password for the username used for authentication.
As a consequence of the username field being left blank, this is also normally blank.
Server
This is an intermediary server through which data is routed. It can be useful by providing security and optimizing network usage.
This option is also mostly left blank by many service providers.
MMSC
Multimedia Messaging Service Center (MMSC) is a setting for handling multimedia messages; Images, videos and audio. It works in combination with other settings like MMS Proxy and MMS Port.
MMSC is normally a url supplied by your carrier.
MMS Proxy
Multimedia Messaging Service Proxy (MMS Proxy) is a setting that routes your MMS messages through a proxy server.
This is normally an IP V4 address of the MMS Proxy server.
MMS Port
Multimedia Messaging Service Port (MMS Port) is the port number of the MMS Server.
It is normally a 2 or 4 digit number, 80 or 8080 in many cases.
MCC
Mobile Country Code (MCC) is a parameter used in configuration of the APN. MCC is a three digit number that identifies the country within the International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) number.
When setting up an APN, MCC is used to identify the correct country in which the mobile device is operating. This helps it connect to the correct mobile network of that country.
MCC for the United States is 310.
MNC
Mobile Network Code (MNC) is a unique 3 digit number that uniquely identifies the mobile network operator combined with the Mobile Country Code (MCC).
In the United States, the MNC for T-Mobile is 260, Verizon is 012 and AT&T is 410.
Authentication type
Authentication type specifies the type of authentication used to connect to services in the network. There are 4 option in the authentication type field:
- None
- PAP (Password Authentication Protocol)
- CHAP (Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol)
- PAP or CHAP
If you do not have a username and password, choose the first; None. Otherwise use PAP or CHAP last option
APN Type
This option defines the type of data services or connections that your device can use within a specific APN configuration. It specifies the kind of data traffic to be carried by the APN configuration.
The options available include:
- default: general internet usage browsing and app usage
- mms: this option is used for sending and receiving multimedia messages
- supl: Secure User Plane Location (SUPL) is useful for improving location services
- dun: Dial-Up Networking (dun) is used for tethering services to a computer
- hipri: High-Priority Mobile Data is used for data services that require higher quality data connections like video streaming
- fota: Firmware Over-The-Air (FOTA) means the current connection can be used for updating firmware
- ims: indicates the APN can be used for IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem) traffic.
- cbs: Carrier Branded Service (CBS)
- ia: Initial Attach (IA)
- xcap: XML Configuration Access Protocol (XCAP) allows a user to read, write and modify application configuration data stored in XML format
- emergency: Indicates APN can be used for emergency PDN Connection.
For many mobile network operators, default and mms are the only two required configurations. The rest work without setting them up and therefore not required unless specifically indicated.
APN Protocol
This option determines the protocol that your device uses to connect to the internet and other data services provided by the mobile carrier. Options available are:
The choice determines the speed and security of the service. Always go with IPv4/IPv6 so the network can automatically pick the best for you. It always prefers IPv6 and when not available it goes back to IPv4.
APN roaming protocol
APN roaming protocol is similar to the APN Protocol option above but is used while out of the primary country of registration. Set the options similar to it; IPv4/IPv6
APN enable/disable
APN is always enabled since you need to use it.
Bearer
Bearer is the virtual communication channel that allows for data transmission. It allows transmission of information signals between network interfaces.
These options are available.
- Unspecified
- LTE
- HSPAP
- HSPA
- HSUPA
- HSDPA
- UMTS
- EDGE
- GPRS
- eHRPD
- EVDO_B
- EVDO_A
- EVDO 0
- 1XRTT
- IS95B
- IS95A
- NR
Always choose the Unspecified option so your device can connect to the fastest available network.
MVNO type
Mobile Virtual Network Operator (MVNO) is a wireless communication service provider that does not own the infrastructure but leases it from an established player.
The options available are
- None
- SPN (Service Provider Name)
- IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity)
- GID (Group Identifier Level 1)
Always choose None unless indicated otherwise by your carrier.
MVNO value
MVNO value allows APN configurations to be restricted for use only when using specific Mobile Network Operators (MNOs). It works hand in hand with MVNO type.