An APN (Access Point Name) is a term used in mobile networking, specifically for cellular data connections. It identifies the gateway between your device and the internet. An IP address (Internet Protocol address), on the other hand, is a unique identifier for devices connected to a network. While an APN doesn’t directly relate to an IP address, they both play crucial roles in connecting your device to the internet.
When you use mobile data, your device sends a request to the APN server with specific information like the IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity) and IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity). The APN then responds by providing an IP address for your device to access the internet. So, while they are not directly related, both the APN and IP address are essential components in enabling mobile data connectivity on your device.

What is an Access Point Name (APN)?
An Access Point Name (APN) is a specific configuration that identifies a particular data network. It acts as a gateway between your mobile device and the internet, allowing you to access various services such as email, web browsing, or messaging. When you connect your mobile device to a cellular network, it automatically searches for an available APN. Once connected, your device can communicate with other devices and servers on the internet using their IP addresses.
Hence, APNs are not IP addresses per se. Instead, they serve as the bridge that enables communication between your device and various IP addresses on the internet. To illustrate this further, consider the following analogy: an APN is like a post office; it’s not a physical location or a number you can dial, but rather a directory that lists all possible destinations (IP addresses) for sending and receiving mail (data packets).
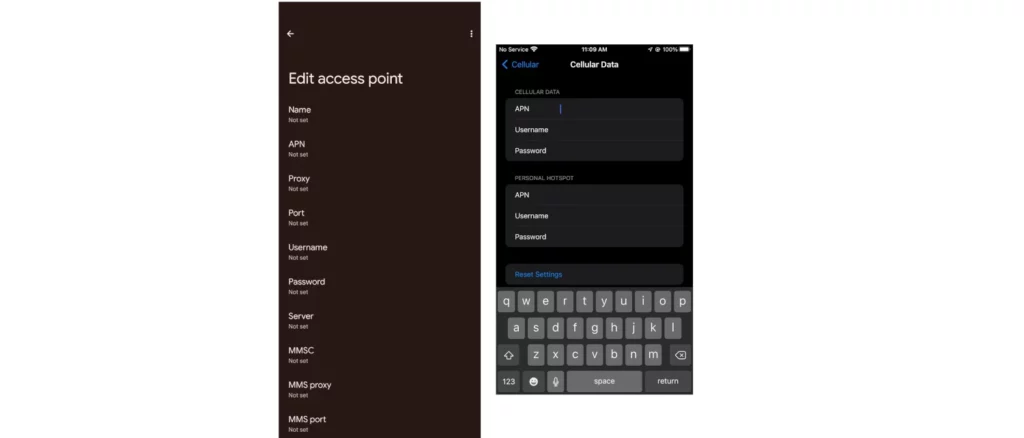
APNs and Cellular Data Connections
When setting up a cellular data connection on your mobile device, the APN configuration is crucial. It determines how your device communicates with the cellular network and accesses various services. For instance, some APNs are designed for specific carriers or mobile plans, while others allow access to particular content providers or third-party applications.
Misconceptions and Common Use Cases
One common misconception is that APNs themselves have IP addresses. However, this is not the case, as an APN is a configuration that facilitates communication between your device and various IP addresses on the internet.
Another use case where APNs come into play is when you’re trying to troubleshoot connectivity issues on a mobile device. In such cases, checking the APN settings can help identify potential problems or misconfigurations that might prevent proper communication with the cellular network and, subsequently, with various IP addresses on the internet.
In conclusion, an Access Point Name (APN) is not an IP address. Instead, it acts as a configuration that identifies a particular data network and facilitates communication between your mobile device and various IP addresses on the internet. Understanding this distinction can help clear up any confusion regarding APNs and their role in mobile communications.