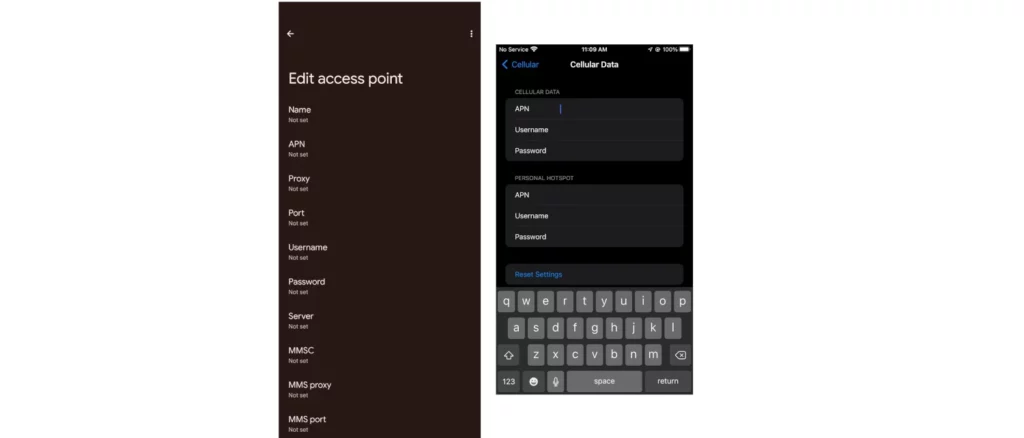
In the world of mobile data communication, Access Point Names (APNs) play a crucial role in establishing and managing connections between mobile devices and cellular networks. APNs act as intermediaries between your device and the internet service provider (ISP), enabling access to various types of network services such as 2G, 3G, 4G, or 5G data, MMS, SMS, and Voice over IP (VoIP). With different mobile operators offering diverse APN configurations, it can be challenging to determine which one is the best fit for your needs. In this article, we will explore the most common types of APNs – default, web, and custom – and discuss their respective advantages and disadvantages.

Understanding Access Point Names (APNs)
Access Point Names (APNs) are unique identifiers assigned to various network services provided by mobile operators. They serve as a bridge between your mobile device and the internet service provider, ensuring smooth communication and data transfer over the cellular network. APNs enable your device to connect to specific services like internet browsing, email, or multimedia messaging.
Three Main Types of Access Point Names (APNs):
Default APN:
A default APN is the one configured by your mobile operator or device manufacturer for general internet access. It covers basic internet connectivity and might not be optimized for specific applications or services. You can check your current default APN settings in your device’s network settings menu. Using a default APN is suitable if you don’t require custom configurations for your mobile data connection.
Web APN:
A web APN, also known as a general packet radio service (GPRS) or internet APN, is designed primarily for web browsing and email services. It may provide better performance for these tasks compared to using the default APN since it is optimized for them. However, web APNs might not support other advanced features like MMS, VoIP, or video streaming.
Custom APN:
A custom APN allows you to configure specific settings tailored to your needs, enabling better control over various aspects of your mobile data connection. Some common uses for custom APNs include:
- Overriding default settings for improved performance and stability, especially in areas with weak signal strength.
- Optimizing connections for VoIP applications like Skype or Zoom.
- Enabling MMS services for sending/receiving multimedia messages.
- d. Configuring APNs for specific devices or applications that require unique settings.
Which Access Point Name (APN) type is best?
The best APN is the one provided by default by your carrier or wireless cellular service provider. These settings are installed automatically when a SIM is inserted to a phone or an eSIM is configured and detected on the network for the first time or when it detects absence of APN settings. The default APN is most preferred since service providers include all required APN settings for data, VoIP, MMS, Email and all network services provided by the network. Custom and Web APNs may not have all updated settings which may leave out some services which makes them to be completely unavailable to users. Only use custom APNs when you are sure about specific services that you are looking for or aware of the ones you are missing.
Choosing the right Access Point Name (APN) for your mobile device depends on your specific needs and usage patterns. While default APNs offer basic connectivity, web APNs can provide better performance for web browsing and email services, and custom APNs give you complete control over advanced settings. Before making a decision, consider evaluating your mobile data requirements and consulting with your mobile operator or network administrator if needed. By understanding the benefits and limitations of each type of APN, you’ll be well-equipped to make an informed choice that maximizes your mobile connectivity experience.