Two essential components often come up in discussions in mobile communication: APN (Access Point Name) and SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) cards. While these terms are related to mobile internet connectivity, they serve distinct functions. In this article, we will explore the relationship between APN and SIM card in detail, clarifying any potential confusion.

What is a SIM Card?
Understanding the Basics of a SIM Card
A Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) card is an integral component of modern mobile communication systems. It contains vital information required for a mobile device to authenticate and identify its user, allowing them access to cellular network services. This includes the phone number, contact list, text messages, and subscription details. When you switch phones, all you need to do is transfer your SIM card to maintain your phone number and personal data.
Role of a SIM Card in Mobile Communication
A SIM card’s primary function is to store subscriber-specific information such as the unique International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) number, which identifies the user, and their phone number. It also stores encryption keys for secure communication between devices and the network. In essence, a SIM card acts as a user ID that enables mobile services by linking your device to the carrier’s network.
What is APN?
An Overview of Access Point Names (APNs)
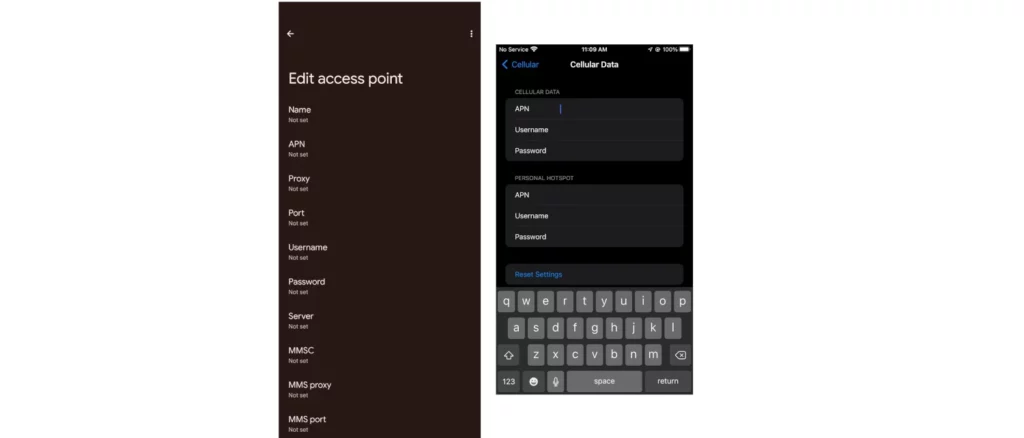
An Access Point Name (APN) is an essential configuration setting that specifies the gateway (a proxy server or a router) through which your device accesses the internet over a cellular network. In simpler terms, it acts as a bridge between your mobile device and the internet service provider (ISP). When you connect to a wireless network like Wi-Fi, there’s no need for an APN since the connection is established through a different protocol. However, when using cellular data, an APN must be configured correctly on your device for a successful connection.
Role of APNs in Mobile Internet Connectivity
APNs play a crucial role in mobile internet connectivity by routing your device’s request to the correct network server. They are often associated with specific services or network types, such as 2G, 3G, 4G, or 5G. For instance, a VoLTE (Voice over Long-Term Evolution) APN is used for making voice calls over 4G networks. Without the correct APN settings, your device may struggle to access the internet over cellular data, leading to connectivity issues.
The Relationship Between APN and SIM Card
Separate but Related Components
Although APNs and SIM cards are related to mobile communication, they serve distinct functions that do not require direct interaction with each other. A SIM card is responsible for storing user-specific information and authenticating the device on a cellular network, while an APN determines how your device accesses the internet over the network. In essence, a SIM card identifies you to the network, and an APN specifies how you connect to the internet via that network.
In conclusion, understanding the relationship between APN and SIM card is essential for anyone who relies on mobile communication for work or personal use. While they may seem related, these two components have distinct functions: a SIM card identifies the user and their device to the network, while an APN determines how the device connects to the internet over that network. By having a clear understanding of each component’s role, you can effectively troubleshoot connectivity issues and ensure optimal mobile performance.